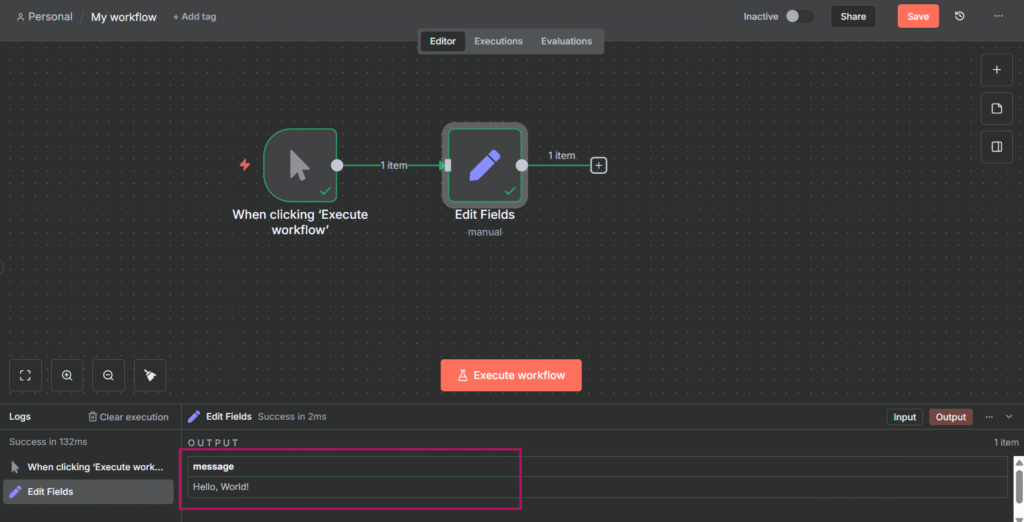
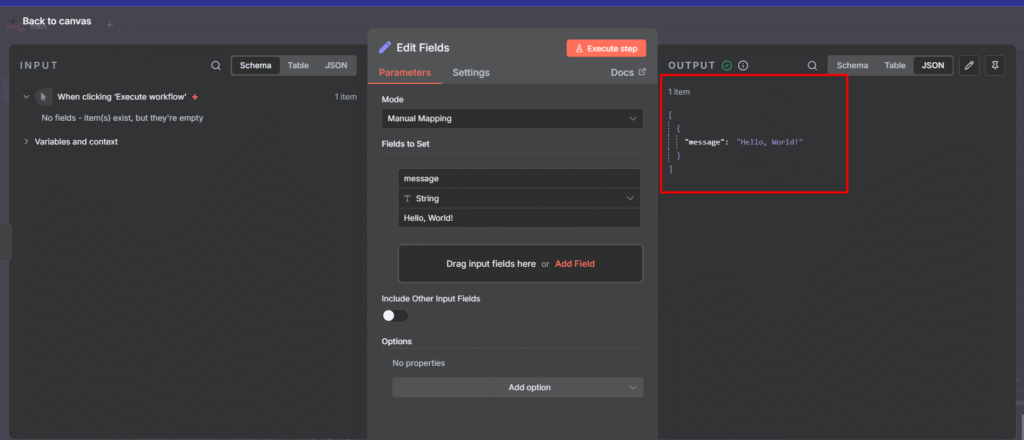
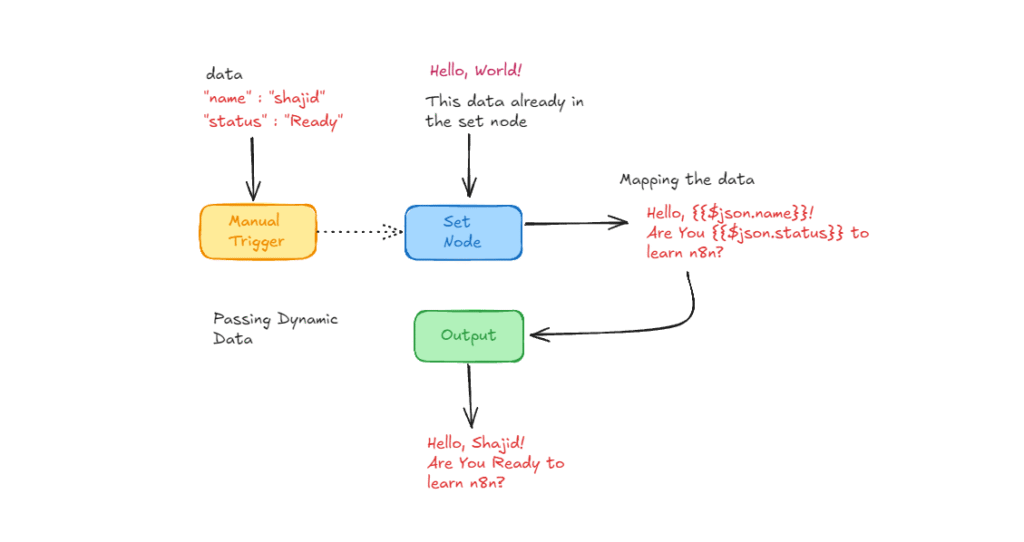
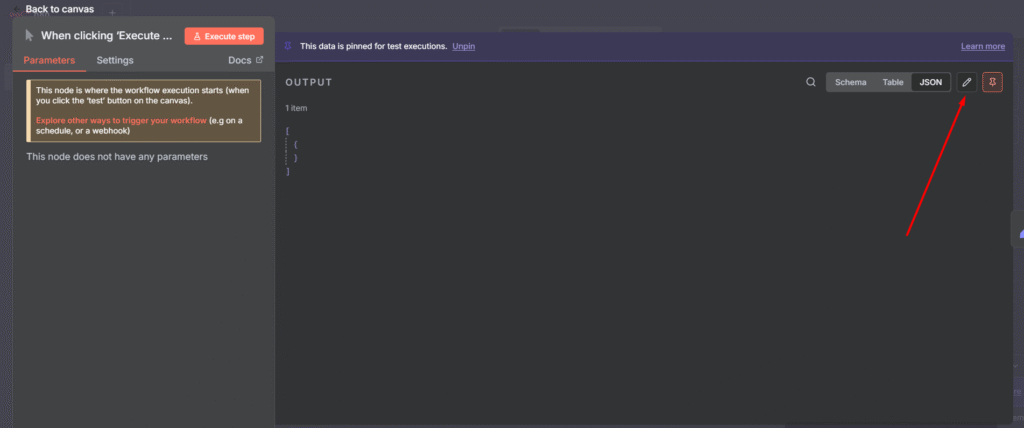
In my previous post, I showed you how to handle rate limits when calling external APIs – It’s a defensive side of rate limiting. Today we are going to learn a production-grade rate limiting with Redis.
Just assume that you’ve created a custom form in WordPress to obtain leads, and of course, you might encounter some unusual form submissions or spams like 10,000 submissions in a minute, but it’s all are worthless leads – To prevent this, we are going to add a guard, that’s going to strictly allow few people only for a certain time period. That’s what it is.
So we are going to build such a handy workflow to handle such attacks efficiently with Upstash + n8n.
Why Redis for Rate Limiting?
I added this sub-heading because one of a commenter in my reddit-post shared the same question? Why redis for rate limiting?
You might be thinking “Can’t I just use n8n’s built-in throttling?”
Aye, sure, for throttling your requests to external APIs, but for protecting such a case I have mentioned above, then you should need a custom solution. That’s where Upstash Redis comes in to the play.
- Persistent State: Data lives outside n8n’s memory. Workflow restarts don’t reset your counters. This is critical for production
- Speed: In-memory operations happens in microseconds. Your rate checks add virtually zero latency to each requests.
- Built-in TTL: Key automatically expires, No clean-up jobs, No database bloat, Set it to 60 seconds. Perfect for time-windowed rate limiting
- Per-use tracking: You can rate limit by email, IP, API Key, or any identifier. Each user get their own counter.
- Atomic Operations: the INCR command is thread-safe, Multiple simultaneous requests won’t break your counter – crucial when handling concurrent requests.
Why Upstash Specifically?
- Serverless (no Redis server to manage or maintain)
- Global edge network (low latency worldwide)
- Generous free tier. (500k commands per month / 50GB Bandwidth)
- Pay as you go – $0.2 / 100k commands
Alright, for our workflow we don’t need the pay as you go, so you can stay for free tier, until you hit the maximum requests. Literally, small to medium sites you’ll stay on the free tier forever.
Understanding Rate Limiting Pattern
Before we dive into the workflow, let’s understand how counter-based rate limiting works, It’s beautifully simple.
- Requests comes in > Extract an identifier (email, IP or API Key)
- Increment counter in Redis > Add 1 to counter, set TTL if it’s a fresh request
- Check the counter > if it’s above your threshold, deny the request
- Allow or deny > Either process the requests or return 429 (Too many requests)
The magic is in the TTL (time to live). When you set 60-seconds TTL, redis automatically deletes the key after 60 seconds. No cleanup needed. The counter resets automatically.
so if someone submits your form at 10:00:00, they can’t submit until 10:01:00. Simple, effective and spam-proof.
Real World Example Workflow
To show you how this works in practice, let’s implement rate limiting for a WordPress website contact form that saves to Google sheet.
This exact pattern works for any API endpoint you need to protect.
- Custom API endpoints
- Webhook receives from external services
- Form submissions (any platform, not just WordPress)
- User action endpoints (voting, commenting, or ordering)
- Data collection endpoints
Our demo scenario
- WordPress contact form submission via Webhook.
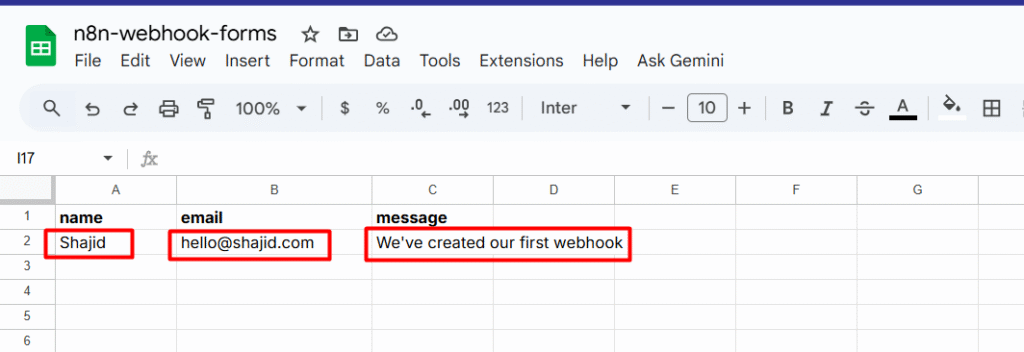
- Data should go to Google Sheet
- Limit: 1 submission per email for 60 seconds
- This protects our Google Sheets API quota and prevent spam
The Workflow
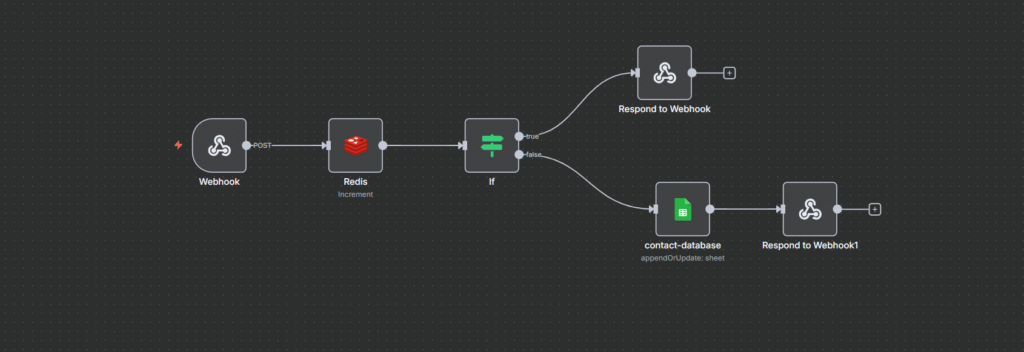
Let’s break down each node and understand the pattern
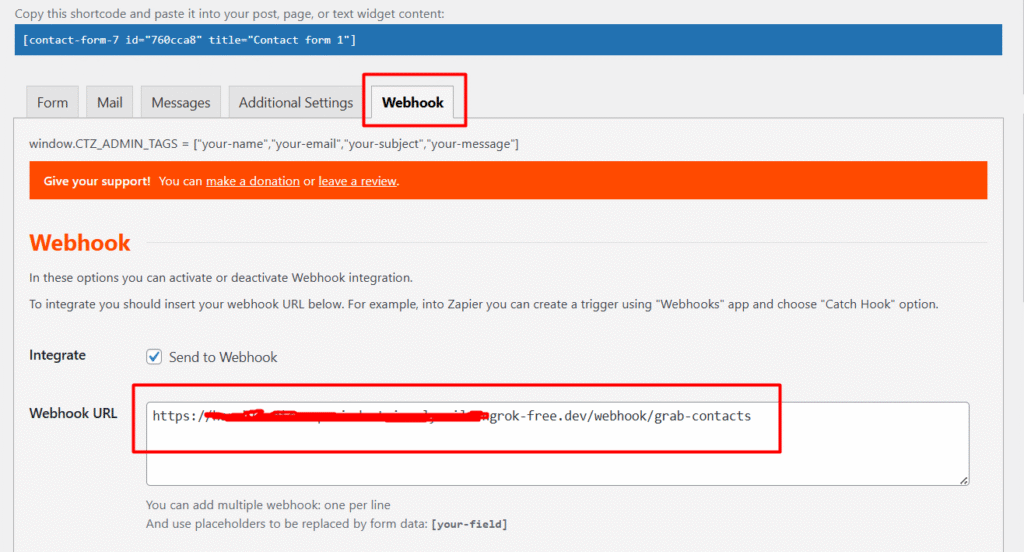
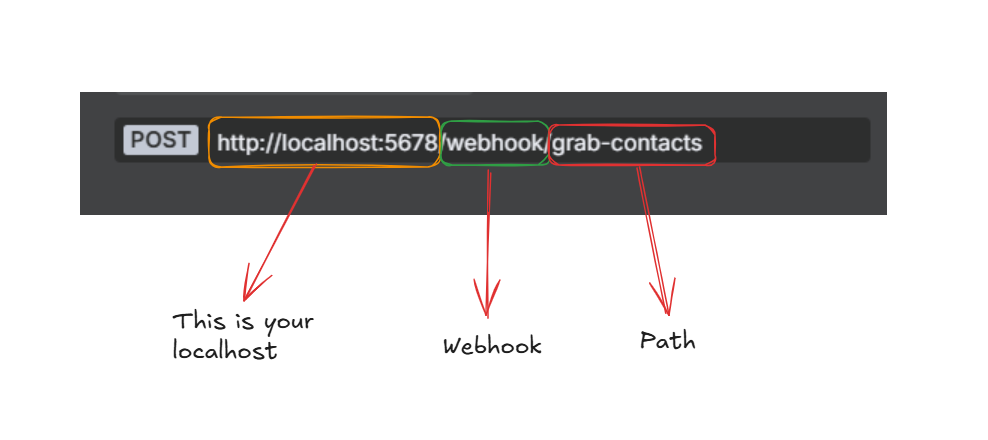
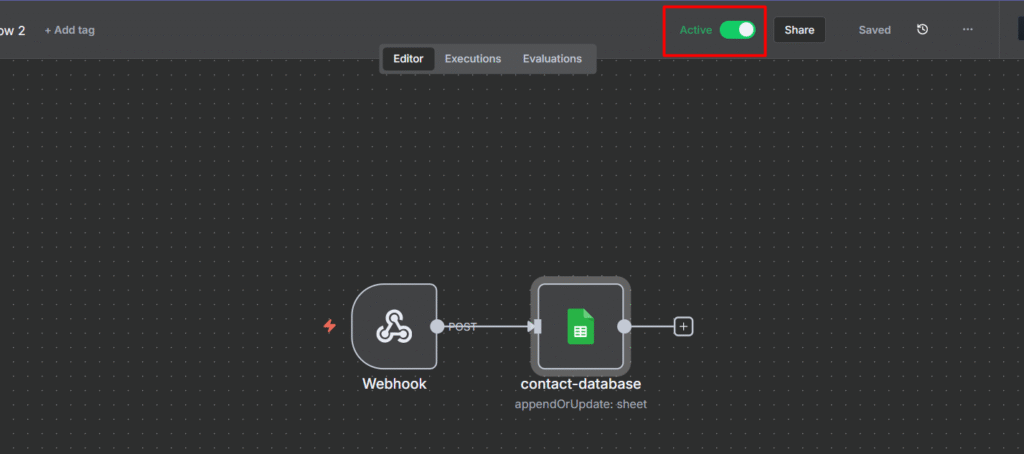
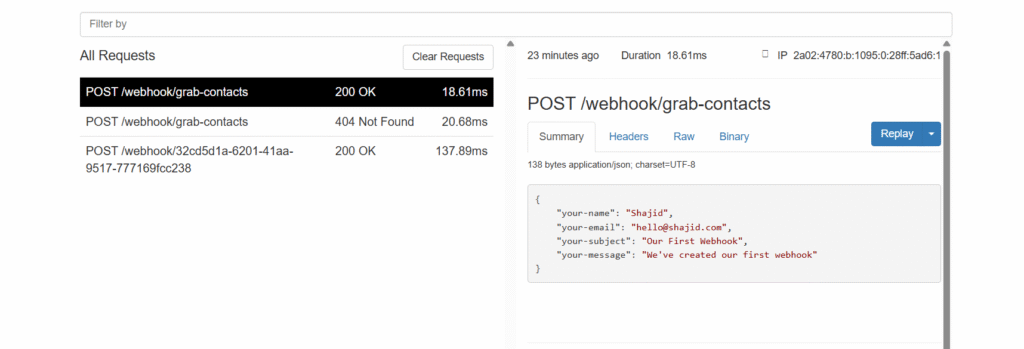
Node 1: Webhook Trigger
This is your entry point, The WordPress form submits data here via a webhook. Could be Contact Form 7, WPForms, Gravity Forms or any form plugin that supports webhook.
Read Here: Webhooks in n8n for Beginners
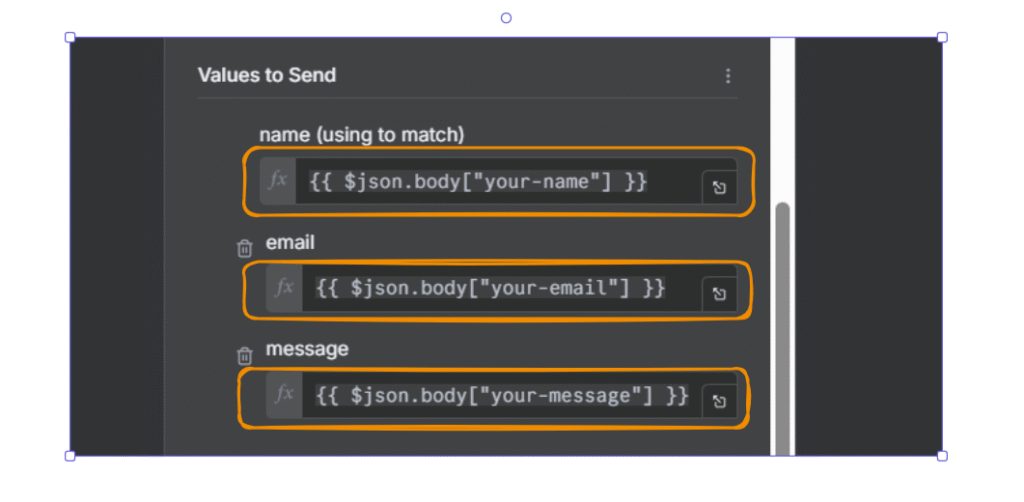
The incoming payload looks something like this
{
"body": {
"your-name": "Shajid Shafee",
"your-email": "Test@ShajidShafee.com",
"your-message": "Hey! This is my first feedback".
}Different form plugins structure their data differently, Some use body.your-email other just use your-email. That’s why we need smart fallback handling in the next step.
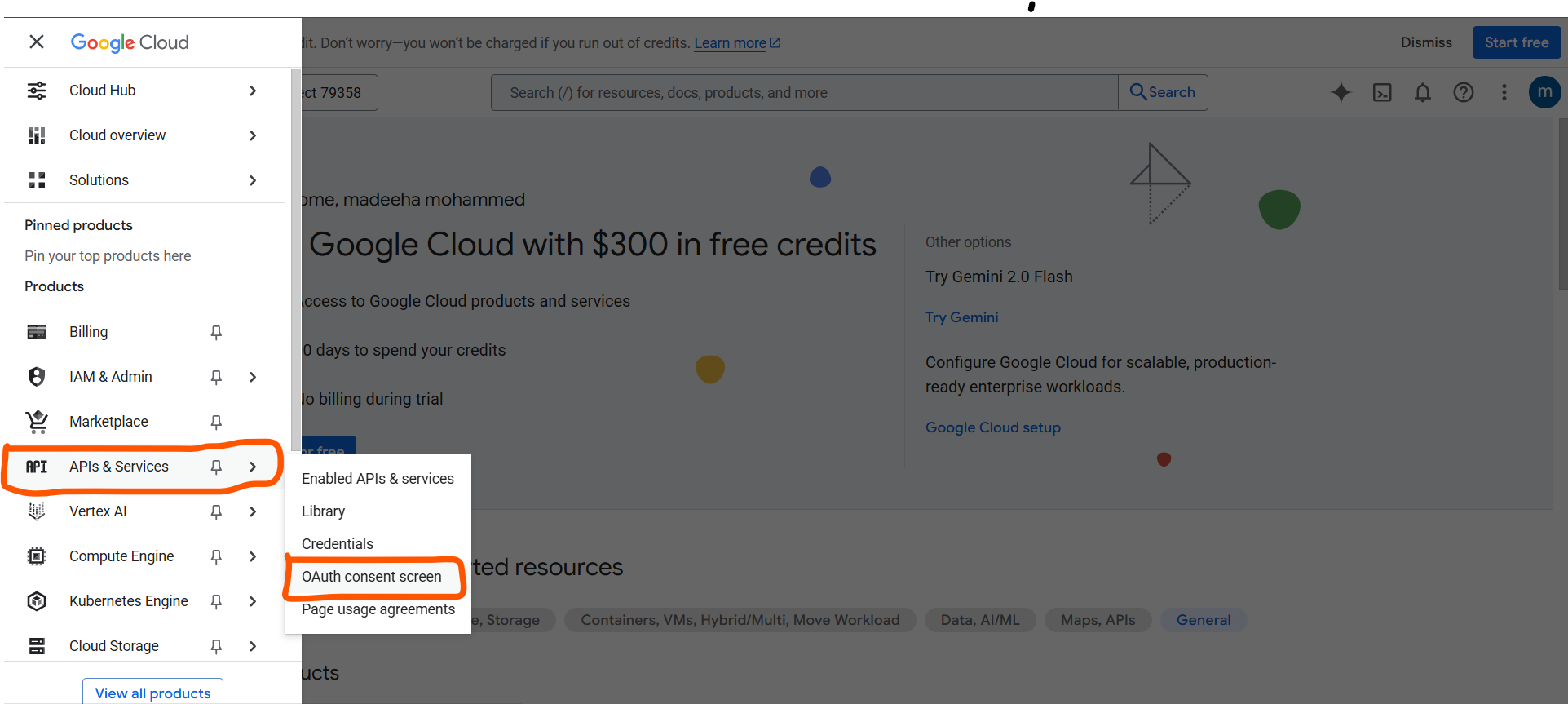
Node 2: Redis Increment
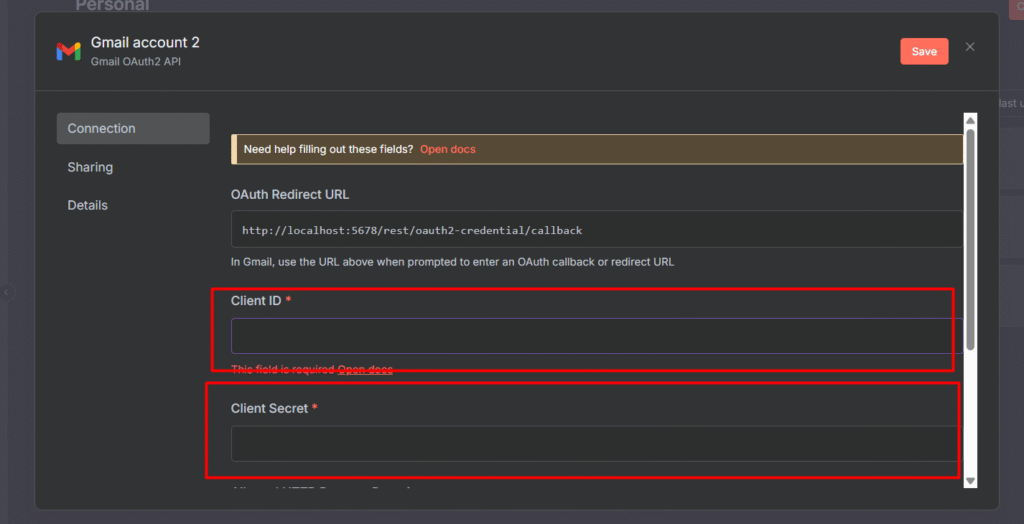
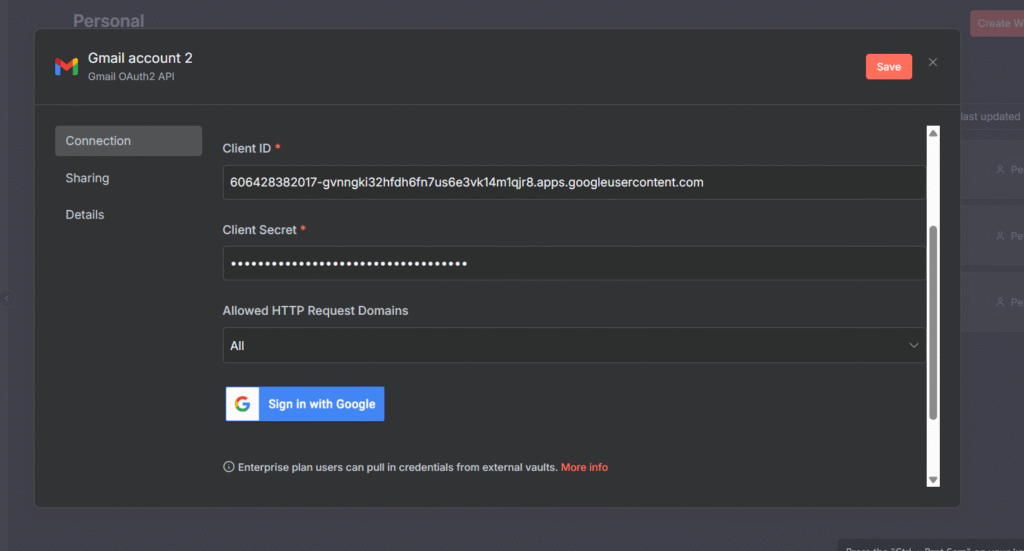
Here’s the steps you need to take to configure Redis Node.
- Step 1: Go to Upstash.com and create a FREE account
- Step 2: Go to your workflow and add a Redis Node
- Step 3: In Upstash, Create database. Give a name, and Select US-East-1 AWS for the server location, and use everything for free.
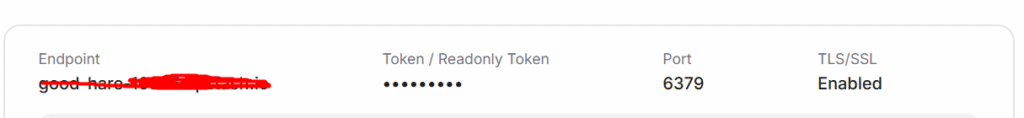
- Step 4: Go to Workflow, Configure the Redis node,
- Host: Paste the endpoint
- Port: 6379
- Password: Paste the Upstash database token
- Database Number: 0
- By adding this save the credentials, you’re good to go
This is where the magic happens. We’re using Redis’s INCR command to atomically increment a counter
Key structure
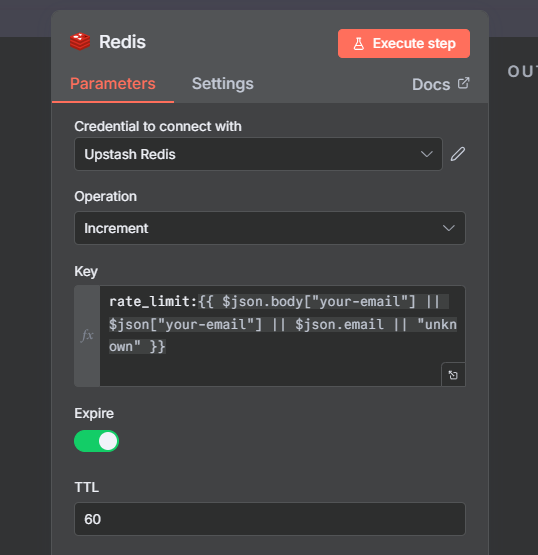
rate_limit:{{$json.body["your-email] || $json["your-email" || $json.email || "unknown"]}}paste the above code block directly on the redis node.
Let’s break down the expression
{$json.body["your-email]– Checks Contact Form 7 format, because I’m using contact form 7|| $json["your-email"]– Fall back for WP Forms|| $json.email– Fall back for other plugins|| "Unknown"– Last resort if no email found
so if the email is john@example.com, your redis key becomes
rate_limit:john@example.comTTL: 60 seconds
This means the key (and its counter) will automatically disappear after 60 seconds. The user can submit again after TTL expire.
What happens in Redis?
- First submission: Key doesn’t exist > Create it, set it to 1, add 60s TTL > Returns 1
- Second submission (within 60 seconds): Key exists > Increment to 2 > Returns 2
- After 60s TTL: Key auto deleted > Next submission for the identifier start fresh at 1
Node 3: Conditional Check (IF)
Now we check the Redis response to decide, allow or deny (rate limit)
Expression
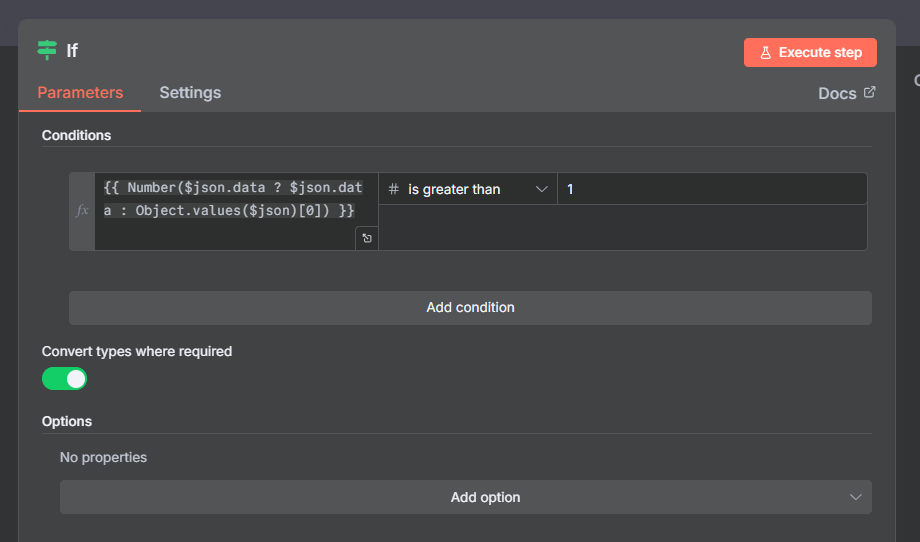
{{ Number($json.data ? $json.data : Object.values($json)[0]) }} > 1This parses the redis response and converts into a Number. then checks if it’s greater than 1
Why > 1 instead of >=2?
Same logic, cleaner to read. If the counter is greater than 1, it means they’ve already submitted once in the last 60 seconds.
- Counter = 1: First submission > False > Allow it
- Counter = 2+: Already submitted > True > Rate Limit
The IF Node has two outputs
- True output (rate limit): Goes to 429 response
- False output (allowed): Goes to Google Sheet
Node 4(a): Rate Limited Path (Responded to Webhook)
When someone hits a rate limit, we return a clear response
{
"error": "Too many requests",
"message": "Rate limit exceeded. try again soon",
}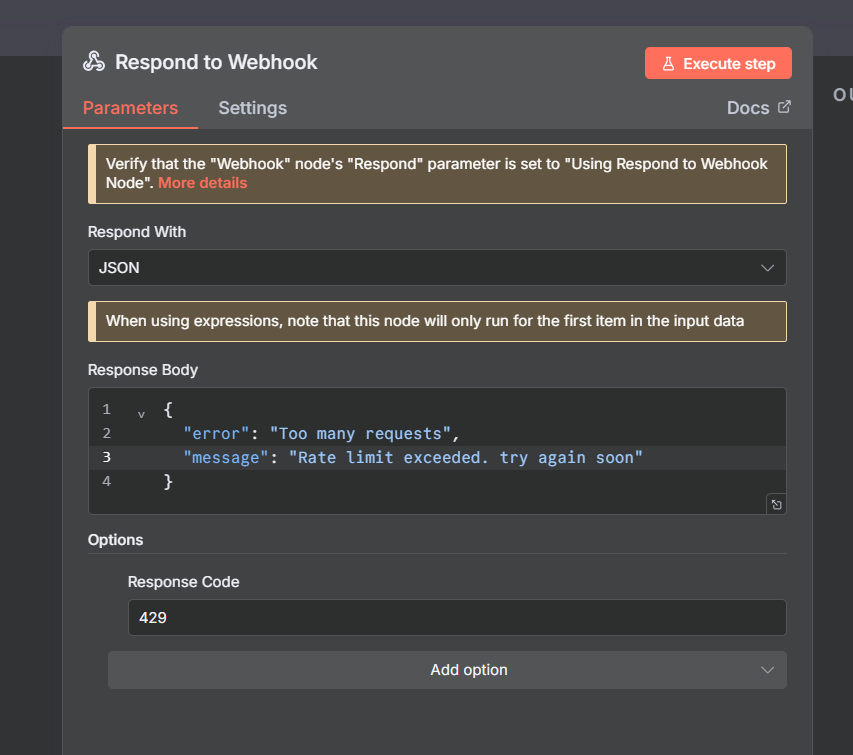
This stops the request. No data reaches your Google Sheet. No email notification sent. Just clean block.
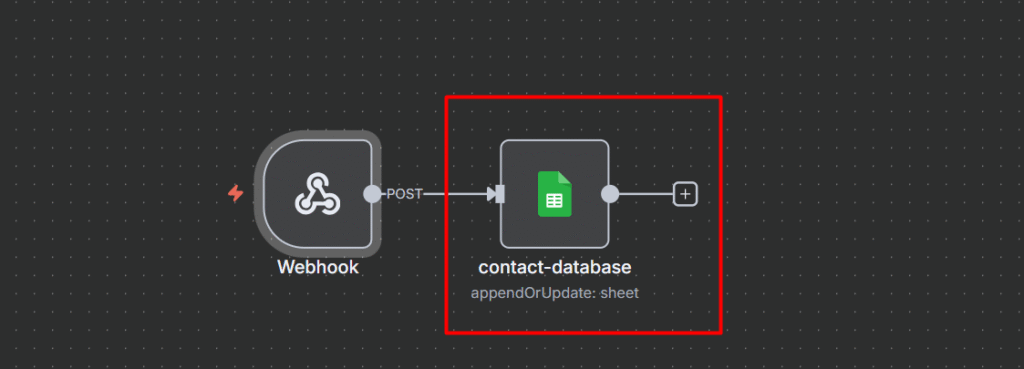
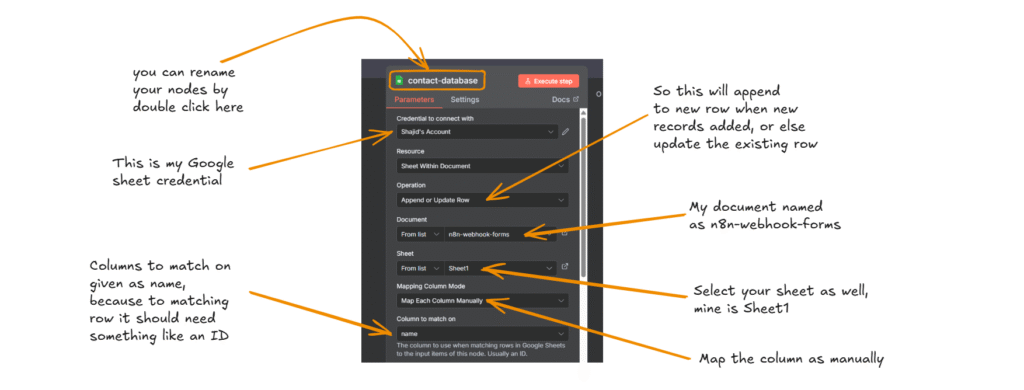
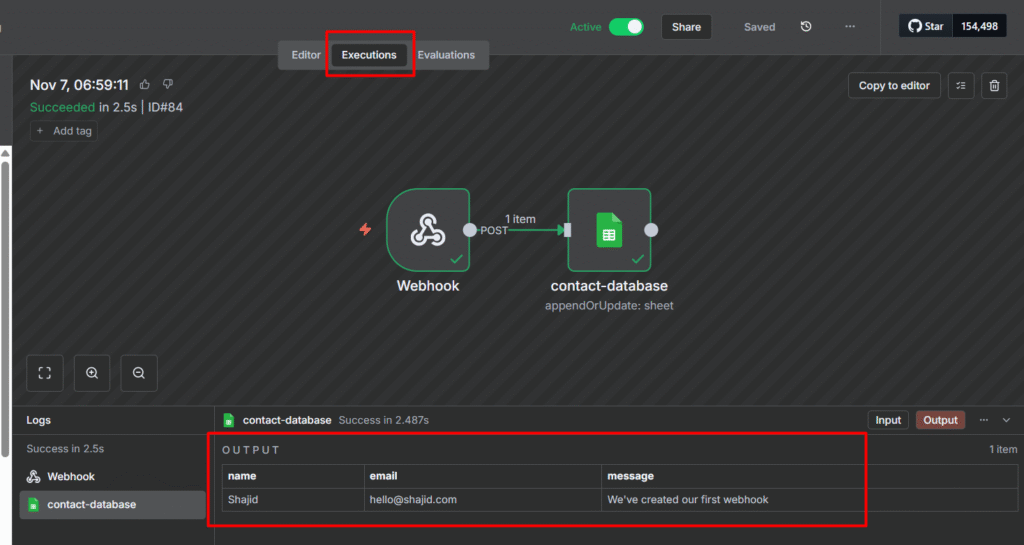
Node 4(b): Success Path
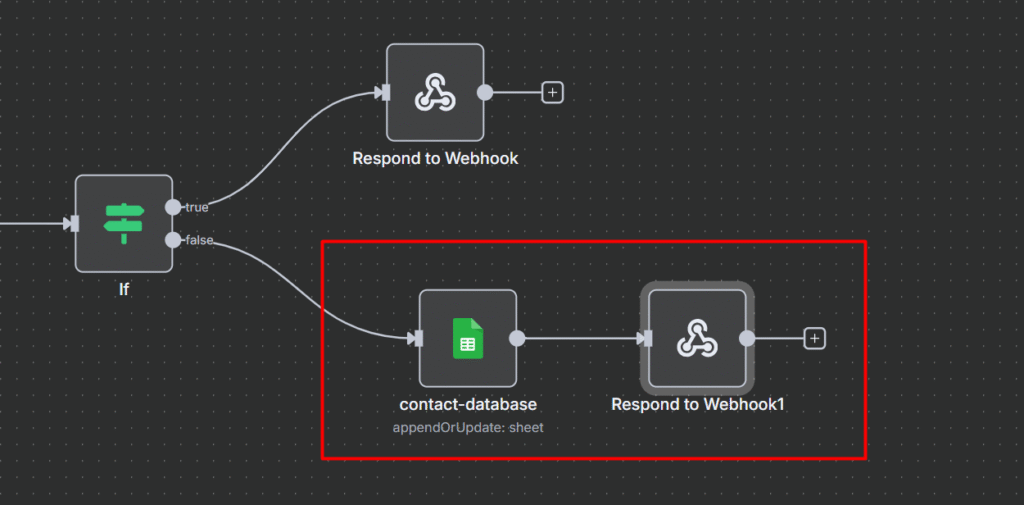
When the request passes the rate limit, we process it normally.
- Google Sheet Node: Append or update the row
- Respond to Webhook: Return success message
Success Response
{ "ok": true, "message": "Form submitted" }The form displays the message to the user, clean, professional. DONE.
Quick Start Checklist
Ready to implement this or to check whether this pattern is actually working.
Setup
- Create upstash account and database
- Copy the endpoint and Token
- Add redis credential in n8n
Build Workflow
- Add Webhook trigger (or any other data source that is sending)
- Add Redis increment node with your key structure
- Add IF condition to check counter
- Add two response nodes 429, and success
- Connect your actual processing (Google sheet, Airtable, or database)
Test
- Send first request > Should Succeed
- Send second request immediately > Should get 429 error
- Wait 60 seconds > Should succeed again
That’s it. Production grade rate limiting is ready to serve.
Conclusion
Rate limiting isn’t just for big tech companies or SaaS platforms. With Upstash Redis and n8n, you can implement production grade rate limiting without writing code.
- Protect any endpoint from abuse (forms, APIs, webhooks, actions)
- Stay within the downstream service quotas (Google Sheet, Airtable, database)
- Prevent spam and bot attacks automatically
- All for $0.00/month on Upstash free tier
- Deploy this workflow in just 15-20 minutes with no infrastructure management
The pattern is dead simple. Increment counter, check threshold, allow or deny. But the application are endless.
Whether you’re protecting a WordPress form, a custom API, a webhook receiver, or user actions – the Redis rate limiting pattern works the same way every time.
Start with the example I showed you, then adapt it to your specific needs and use case. You just connect the dots in n8n.